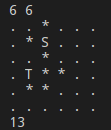前面介绍广度优先算法的时候提及了多次走迷宫,我们就真正的走一次迷宫试试!
要求如下:
输入给出迷宫矩阵的行数和列数,并给出迷宫(使用点 (.) 表示路,使用星 (*) 表示障碍物,使用S表示起点,T表示终点)
例如:
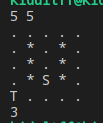
5 5
. . . . .
. * . * .
. * S * .
. * * * .
. . . T *
输出最短路径的长度。上面的例子中,路线使用原谅绿来表示,长度为11。
根据BFS算法可以很轻松的写出这个程序:
#include <iostream>
#include <queue>
using namespace std;
int m, n;
/*表示坐标的结构*/
typedef struct{
int x, y;
} point;
point start, endp; //起点和终点
/*表示地图上每个点的结构。is_ob表示是不是障碍物(*),
is_checked表示是否检查过该点,step为起点到这一点最少步数*/
typedef struct{
bool is_ob, is_checked;
int step;
} node;
/*map:全局地图*/
node map[100][100];
/*裁定函数,越界返回假,检查过(is_checked==true)返回假,是障碍物(is_ob==true)返回假*/
bool judge(int x, int y){
if(x >= n || x < 0 || y >= m || y < 0) return false;
return !(map[x][y].is_checked) && !(map[x][y].is_ob);
}
/*偏移量*/
int X[] = {1, -1, 0, 0}, Y[] = {0, 0, -1, 1};
/*广度优先算法*/
int BFS(int x, int y){
/*到终点的最少步数*/
int result = 0;
queue<point> Q;
point P;
P.x = x, P.y = y;
Q.push(P);
map[x][y].is_checked = true;
int top_step = 0;
while(!Q.empty()){
point top = Q.front();
Q.pop();
if(top.x == endp.x && top.y == endp.y) //是终点,返回步数
return top_step;
for(int i = 0; i < 4; i++){
top_step = map[top.x][top.y].step;
int newX = top.x + X[i], newY = top.y + Y[i];
//printf("队首(%d,%d),正在检查(%d,%d)",top);
if(judge(newX, newY)){
map[newX][newY].step = top_step + 1;
P.x = newX, P.y = newY;
Q.push(P);
map[newX][newY].is_checked = true;
}
}
}
}
int main(){
cin >> n >> m;
char c;
for(int y = 0; y < n; y++)
for(int x = 0; x < m; x++){
cin >> c; //读入该点
if(c == '*'){ //是障碍物
map[x][y].is_ob = true;
map[x][y].is_checked = false;
}else{ //不是障碍物
map[x][y].is_ob = false;
map[x][y].is_checked = false;
}
if(c == 'S') //起点
start.x = x, start.y = y;
if(c == 'T') //终点
endp.x = x, endp.y = y;
map[x][y].step = 0;
}
cout << BFS(start.x, start.y) << endl;
return 0;
}运行结果: