There is a kind of balanced binary search tree named red-black tree in the data structure. It has the following 5 properties:
-
(1) Every node is either red or black.
-
(2) The root is black.
-
(3) Every leaf (NULL) is black.
-
(4) If a node is red, then both its children are black.
-
(5) For each node, all simple paths from the node to descendant leaves contain the same number of black nodes.
For example, the tree in Figure 1 is a red-black tree, while the ones in Figure 2 and 3 are not.
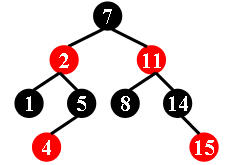 |
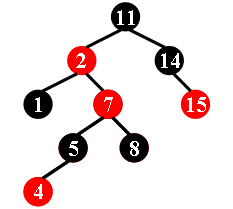 |
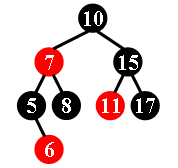 |
|---|---|---|
| Figure 1 | Figure 2 | Figure 3 |
For each given binary search tree, you are supposed to tell if it is a legal red-black tree.
Input Specification:
Each input file contains several test cases. The first line gives a positive integer K (≤30) which is the total number of cases. For each case, the first line gives a positive integer N (≤30), the total number of nodes in the binary tree. The second line gives the preorder traversal sequence of the tree. While all the keys in a tree are positive integers, we use negative signs to represent red nodes. All the numbers in a line are separated by a space. The sample input cases correspond to the trees shown in Figure 1, 2 and 3.
Output Specification:
For each test case, print in a line "Yes" if the given tree is a red-black tree, or "No" if not.
Sample Input:
3
9
7 -2 1 5 -4 -11 8 14 -15
9
11 -2 1 -7 5 -4 8 14 -15
8
10 -7 5 -6 8 15 -11 17Sample Output:
Yes
No
No题目大意:判断是不是红黑树。
红黑树有以下特征:
-
每个节点不是红色就是黑色
-
根节点必须是黑色
-
定义NULL节点为黑色
-
红色节点的孩子必须都是黑色
-
从任意一点出发,到每一个叶子,途经黑色节点的数量必须均相同
-
是搜索树
给定若干二叉树的前序遍历序列,以正数表示黑,负数表示红(树上的真实值都是正数,正负号仅用于区分颜色),判断这棵树是不是红黑树
首先,这个不是完全二叉树,所以肯定是要建树的吧~那我们先建树:
红黑树的特征的第6条是我加上去的,很多人看了题不知道怎么建树。其实题目说了,There is a kind of balanced binary search tree。
所以使用二叉搜索树的特征建树就可以了,比根小,往左插,反之往右插。
接着我们判断根节点,root->data如果小于0了,根节点就是红色的,直接fuck掉就好了
这时,条件1、2、3、6我们满足了,还剩4和5,先从比较简单的4入手。
红色节点的孩子必须是黑色,这很好办,直接把所有红色节点遍历一遍,看看孩子是不是都是正数或NULL就好了。
接着解决条件5,条件5稍有点复杂,但是我们可以使用bfs来解决,使用bfs算法遍历二叉树,遍历的过程记下来途径多少黑色节点,遍历到NULL了,我们判断以下和别的路径遍历到的黑色节点数目是否一致就好了~
根据上面分析,可以写出如下代码:
#include <iostream>
#include <bits/stdc++.h>
using namespace std;
struct node{
int data;
node *lchild, *rchild;
};
void Insert(node* &root, int data){
if(root == NULL){
root = new node;
root->data = data;
root->lchild = root->rchild = NULL;
}else{
if(abs(data) < abs(root->data)) Insert(root->lchild, data);
else Insert(root->rchild, data);
}
}
//红节点孩子一定是黑色
bool JudgeChild(node* root){
if(root == NULL) return false;
if(root->lchild != NULL) //判断左孩子
if(root->data < 0 && root->lchild->data < 0) return true;
if(root->rchild != NULL) //判断右孩子
if(root->data < 0 && root->rchild->data < 0) return true;
//递归检查左右孩子
return JudgeChild(root->lchild) || JudgeChild(root->rchild);
}
//tmpcnt为遍历时黑节点的计数器,cnt存放到达叶子节点的时候有多少黑节点
//如果遍历到叶子节点,tmpcnt与上次遍历得到的cnt不等,说明到达叶子节点的路径中,黑节点数量不等
int tmpcnt = 0, realcnt = -1;
bool dfs(node* root){
if(root == NULL){ //递归边界
//printf("到叶子了,总共%d个黑节点\n", tmpcnt);
if(realcnt == -1) //第一次到达叶子节点
realcnt = tmpcnt; //记录有多少黑节点
else if(realcnt != tmpcnt)//和别的路径得到的黑节点数量不符
return true; //不是红黑树
return false;
}
if(root->data > 0) tmpcnt++; //当前节点为黑节点
//递归遍历左右子树
if(dfs(root->lchild)) return true;
if(dfs(root->rchild)) return true;
if(root->data > 0) tmpcnt--; //dfs完成
return false;
}
int main(){
int cnt;
cin >> cnt;
for(int i = 0; i < cnt; i++){
int _cnt;
cin >> _cnt;
node *T = NULL;
for(int j = 0; j < _cnt; j++){
int __n;
cin >> __n;
Insert(T, __n);
}
tmpcnt = 0, realcnt = -1;
if(T->data < 0 || JudgeChild(T) || dfs(T)) cout << "No" << endl;
else cout << "Yes" << endl;
}
return 0;
}上述代码为了更易于理解,把判断孩子颜色和判断路径上黑节点的数量分开遍历,其实可以写到一起,节省时间:
#include <iostream>
#include <bits/stdc++.h>
using namespace std;
struct node{
int data;
node *lchild, *rchild;
};
void Insert(node* &root, int data){
if(root == NULL){
root = new node;
root->data = data;
root->lchild = root->rchild = NULL;
}else{
if(abs(data) < abs(root->data)) Insert(root->lchild, data);
else Insert(root->rchild, data);
}
}
int tmpcnt = 0, realcnt = -1;
bool dfs(node* root){
if(root == NULL){ //递归边界
if(realcnt == -1) //第一次到达叶子节点
realcnt = tmpcnt; //记录有多少黑节点
else if(realcnt != tmpcnt)//和别的路径得到的黑节点数量不符
return true; //不是红黑树
return false;
}
//判断颜色
if(root->lchild != NULL) //判断左孩子颜色
if(root->data < 0 && root->lchild->data < 0) return true;
if(root->rchild != NULL) //判断右孩子颜色
if(root->data < 0 && root->rchild->data < 0) return true;
//继续判断路径
if(root->data > 0) tmpcnt++;
if(dfs(root->lchild)) return true;
if(dfs(root->rchild)) return true;
if(root->data > 0) tmpcnt--;
return false;
}
int main(){
int cnt;
cin >> cnt;
for(int i = 0; i < cnt; i++){
int _cnt;
cin >> _cnt;
node *T = NULL;
for(int j = 0; j < _cnt; j++){
int __n;
cin >> __n;
Insert(T, __n);
}
tmpcnt = 0, realcnt = -1;
if(T->data < 0 || dfs(T)) cout << "No" << endl;
else cout << "Yes" << endl;
}
return 0;
}
